
For example, if 25,000 units are sold, the company will be operating at 15,000 units above its break-even point and will earn a profit of Rs 1, 50,000 (15,000 units x Rs 10 contribution margin). The profits will be equal to the number of units sold in excess of 10,000 units multiplied by the unit contribution margin. If they fail to achieve this target, a loss will be incurred. If the company manages to sell more than 10,000 units, it will earn profits because fixed costs remain constant. The break-even sales to cover fixed costs will be 10,000 units.īreak-even volume = Rs 1,00,000 fixed cost/Rs 10 contribution margin = 10,000 units Examples of common variable costs include labour directly involved in a company's manufacturing process and raw materials.Īssume that a company manufactures and sells a single product as follows: Variable costs are costs that change with the quantity of output. Examples of Fixed cost include rent, insurance premiums, or loan payments. Fixed costs are costs that do not change with the quantity of output. But, before that, we must understand what fixed costs and variable costs are. Since the basic idea to determine the break-even point is to calculate the point at which revenues begin to exceed costs, the first step is to separate a company's costs in to those that are variable and those that are fixed.
Reducing the amount of fixed costs/expenses.Here’s how cutting cost affects break even point:
#Break even point formula graph khan academy how to#
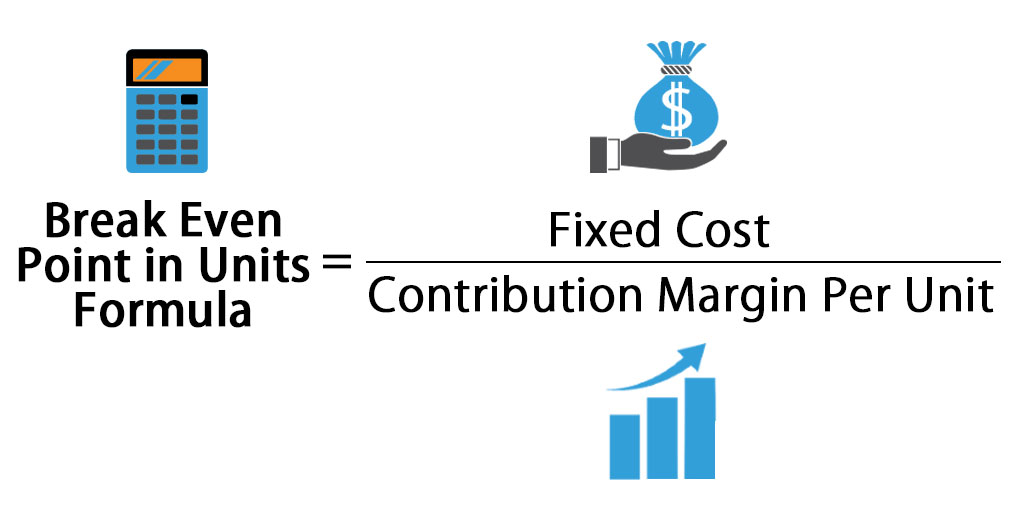
How to calculate break even point?īreak even point can be calculated using the following formula:īreak-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs ÷ (Revenue per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit) How cutting costs affects the break even point? Therefore, comparison of break-even points is generally most meaningful among companies within the same industry, and the definition of a "high" or "low" break-even point should be made within this context. However, typical variable and fixed costs differ widely among industries. Since the price per unit minus the variable costs of product is the definition of the contribution margin per unit, you can simply rephrase the equation by dividing the fixed costs by the contribution margin.īreak-even analysis helps in business owners take crucial decisions like at what price should a product or service be sold at. Let’s look at a few of them as well as an example of how to calculate break-even point. There are several ways to use this concept. Since the expenses are greater than the revenues, these products great a loss-not a profit. Many products cost more to make than the revenues they generate. Not all revenues result in profits for the company. The main thing to understand in managerial accounting is the difference between revenues and profits.

The purpose of the break-even analysis formula is to calculate the amount of sales that equates revenues to expenses and the amount of excess revenues, also known as profits, after the fixed and variable costs are met. For example, a company has a fixed cost of Rs.0 (zero) will automatically have broken even upon the first sale of its product. Generally, a company with low fixed costs will have a low break-even point of sale. Break-even is a situation where you are neither making money nor losing money, but all your costs have been covered.īreak-even analysis is useful in studying the relation between the variable cost, fixed cost and revenue. To put simply, break-even point analysis will tell you the number of products or services a company should sell to cover its costs, particularly fixed costs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
